Introduction to Email Protocols: SMTP, IMAP, and POP3
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Email Protocols: SMTP, IMAP, and POP3
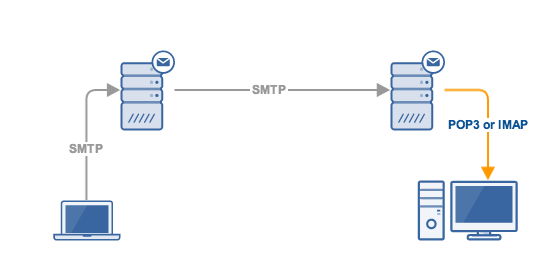
Nowadays, emails have become an indispensable means of communication in both personal and professional spaces. Integral to how emails function are certain protocols, namely the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP), and Post Office Protocol version 3 (POP3). These rules or guidelines dictate how emails are sent, received, and stored. Let’s delve deeper and illuminate these foundational elements.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) - The Outgoing Protocol
SMTP, known as the protocol for outgoing mail, works by sending your email to the server, which the recipient’s client then retrieves using IMAP or POP3. Typically, SMTP uses port 25, while the secure version operates through port 465.
How SMTP Works
When you hit the send button, SMTP springs into action, transferring your email to the intended server. Whether it’s a simple text email or one rife with attachments, SMTP plays a crucial role in getting your message across.
IMAP: For Efficient Email Management
The current version of IMAP in use is the fourth iteration. It works efficiently by downloading a copy of emails while retaining the originals on the server. The standard version of IMAP uses port 143, while the secure version uses port 993.
Advantages and Use of IMAP
IMAP has many advantages. It’s especially useful when you are using multiple devices to access your email. Since a copy of the received emails remains on the server, you can access it from different devices without issues.
POP3: The Basic Email Retrieval Protocol
While IMAP downloads a copy of emails, POP3 operates differently. It pulls emails down while deleting them from the server. POP3 does not handle multiple devices well. In terms of ports, POP3 uses port 110, and its secure version uses port 995.
Why POP3 May Not Be Ideal
POP3 method becomes inefficient if you often use more than one device to access your emails. As POP3 deletes the original email from the server after download, it poses challenges when trying to access emails from different devices.
Before the SMTP vs IMAP vs POP3 debate confuses you further, it’s crucial to note that these protocols are not in competition but work together to ensure smooth email communication from the sender to the recipient. Your understanding of these protocols guides you in optimizing your device’s email settings to meet your communication needs.
